What Is User Lifecycle Management? Our Best Practice Guide
In a professional IT setting, managing the full lifecycle of users and digital identities is critical to maintaining a productive and secure work environment. From an employee’s first to final day, their accounts and privileges need to match their role in the organization. So how do you manage user lifecycles correctly and what are the best practices admins need to know?
What Is User Lifecycle Management?
As an organization, your workforce is constantly changing. Employees join, they transition to new roles and departments and eventually leave your org. And at every stage of their employment, users need the right level of access to IT resources.
User lifecycle management (ULM) is the process of equipping new users with the accounts and privileges they need, updating their access as responsibilities evolve and revoking access when users depart. It is also known as account lifecycle management or identity lifecycle management.
While the tasks involved in on/offboarding users and updating access can be carried out by hand, there are significant advantages to streamlining user lifecycle management through an Identity Governance & Administration solution.
User Lifecycle Management Phases
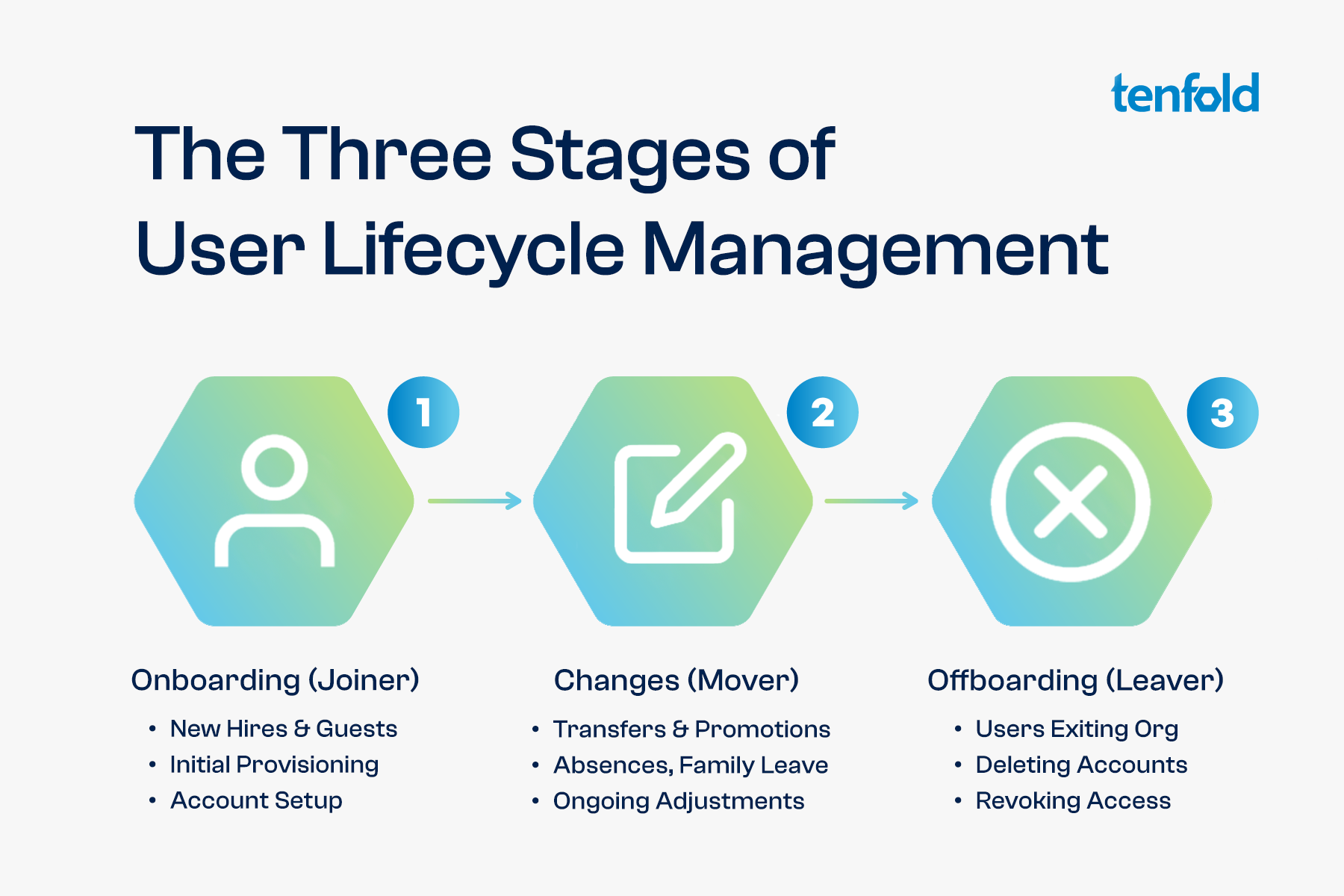
The User Lifecycle can be broken down into three stages, which are also known as the joiner-mover-leaver or JML process. New employees are hired (Joiners), existing users switch to different departments (Movers) and exiting employees need to be offboarded (Leavers).
User Onboarding
During the onboarding process, new users must be provided with the accounts and privileges they need for their job role. This is also known as provisioning. To onboard new users effectively, organizations need to understand which access rights are required by different roles, ensuring access remains appropriate and follows the principle of least privilege.
Onboarding can then be streamlined by creating sets of permissions based on job roles rather than assigning access individually for each IT resource. This approach is also known as role-based access control.
User Management
Even once the initial onboarding has been completed, the user lifecycle includes ongoing changes that require regular adjustments. For example, an employee might transfer from Sales to Product Management, meaning there are some shared privileges they would retain, some new privileges that need to be added and some old privileges that need to be revoked.
Aside from transfers and promotions, another common transition in the user lifecycle are extended absences such as parental leave, medical leave, sabbaticals or trainings, which may require organizations to temporarily suspend access.
User Offboarding
The last stage in the user lifecycle takes place when an employee leaves your organization, at which point their accounts need to be closed, access needs to be revoked and physical assets like keycards and devices need to be collected.
User offboarding must be completed quickly to prevent exiting team members from abusing access before it is deactivated. At the same time, offboarding procedures need to be thorough to ensure that no leftover accounts or privileges remain active. Orphaned accounts are a popular entry point for attackers, since there is no real user behind them to report suspicious activity.
Advantages of Effective User Lifecycle Management
User lifecycle management is an essential task for any IT environment. For your staff to get any work done at all, you need to provide them with the right accounts and access to the right systems.
However, organizations that manage user lifecycles by hand often struggle with the huge burden this places on their IT team, especially as your org scales up. With hundreds of users and dozens of unique apps, manual onboarding and offboarding becomes a huge time sink.
There are significant advantages to automating user lifecycle management through an IGA solution, including:
Appropriate access at all times: Automated lifecycle management ensures that the right users have access to the right resources at the right time. As users join, move and leave, access is dynamically updated to match their current role.
Lower IT workload: Thanks to automated on/offboarding, your IT staff no longer has to spend time manually setting up accounts or updating permissions. This frees them up to focus on more important projects.
Centralized reporting & auditing: IGA not only handles user lifecycles for you, it acts as central hub for everything related to user access. Keep track of user, object and app level permissions with a clear, central breakdown.
User Lifecycle Management: Best Practices
Role-Based Access
Individually assigning users all the access they need makes onboarding a slow, tedious and error-prone process. Role-based access control offers a streamlined approach to both provisioning and ongoing changes. First, you create sets of privileges to match the access needs of different jobs and departments.
These permission roles bundle together everything the user needs to work in that specific role. So by adding a new employee to the role that matches their job, they automatically receive the right level of access. Plus, you get to skip manual provisioning.
In on-prem Windows environments, you can implement role-based access using the AGDLP model. In Microsoft 365, you can likewise use (dynamic) group membership or entitlement management features such as access packages to build out role-based access.
But the best approach to implementing RBAC is through an identity governance & administration solution like tenfold. A dedicated IGA platform has two major advantages over piecing together built-in features:
IGA allows you to govern all IT systems through a single platform.
IGA combines role-based access with comprehensive governance features like access reviews and centralized reporting.
HR Integration
One of the biggest stumbling blocks in user lifecycle management is communication between HR and IT. If your IT team is only informed of a new hire minutes before they walk in the door, this does not give them enough time to complete onboarding procedures. The same is true when news of a department change or exiting employee gets lost in the shuffle. The flow of information is critical.
Luckily, this whole issue can be avoided by tapping directly into your HR software for up-to-date employee information. An IGA solution with HR integration can automatically detect workforce changes and trigger the the necessary on/offboarding workflows.
Access Governance Best Practices for Microsoft Environments
Everything you need to know about implementing access control best practices in Active Directory, from implementation tips to common mistakes.
Self-Service Requests
Role-based provisioning is a great way to quickly and easily assign the baseline access users need for their job. However, users will sometimes need additional permissions on top of their role to work on specific projects, collaborate with other departments or fill in for on of their colleagues.
Dealing with access requests is a normal part of governing IT privileges. Despite this, many organizations struggle with keeping track of these additional permissions. Without a structured process for submitting, approving, granting and documenting access requests, orgs often rely on emails, slack messages or spreadsheets instead.
A more sophisticated approach to access requests should include both a self-service portal giving end users a clear touchpoint for submitting requests and customizable approval workflows, which allow IT staff to delegate requests to stakeholders within departments.
Access Reviews
To ensure that each user has only access rights appropriate for their job position, access not only needs to be updated as users transition to different lifecycle phases. It also needs to be audited regularly.
Access reviews are a periodic audit of all IT permissions designed to remove unwanted access and prevent privilege creep, the steady buildup of privileges that occurs when new permissions are assigned but outdated access is never revoked.
Unfortunately, access reviews are virtually impossible to conduct without a governance solution. Role-based access and automated provisioning can help you reduce the scope of audits, but even so, the number of accounts and privileges to go through is simply too high.
Thankfully, an IGA platform will automatically track which permissions need to be audited and send out clear, actionable checklists to streamline the review process.
Automated Deprovisioning
When a user is missing privileges they need for their work, they will make themselves heard. But when a user leaves and their access remains active, no one will raise the alarm. This makes orphaned accounts silent, but dangerous.
Accounts left behind after termination can be abused by former employees becoming insider threats. Moreover, these abandoned accounts increase the attack surface of your organization. And if an abandoned account is breached, there is no real user on the other side to report suspicious activity.
To combat these risks, it is essential that employees are fully deprovisioned as soon as they leave the organization. On paper, most orgs understand this. But in practice, it’s easy to forget steps in the offboarding process or miss an account, especially when you have no idea which accounts and privileges your users actually have.
The best way to avoid mistakes in the offboarding process is to automate deprovisioning entirely. Just as an IGA solution can automate the rest of the user lifecycle by detecting changes in your HR database and updating access as needed, so too can it close accounts and revoke privileges when users leave your org. Automated deprovisioning is more than just a time saver, it is essential to security and compliance.
Manage User Lifecycles with Ease with tenfold IGA
From streamlining provisioning with access roles to delegating approval workflows to stakeholders within departments, there are many steps you can take to simplify user lifecycle management.
But by far the biggest productivity boost you can achieve is to fully automate user lifecycles using an IGA solution. If your IT team spends countless hours onboarding new users or playing catch-up with changes, transfers and departures, then investing in an IGA tool is a no-brainer!
With tenfold, IGA has never been easier. Thanks to our no-code interface and out-of-the-box support for Active Directory, Microsoft 365 and common workplace apps, setting up tenfold is a breeze. tenfold offers comprehensive Identity Governance & Administration in as little as 2 weeks when other solutions take months or years to deploy.
Don’t waste your time on endless setups: Book a personal demo today to see why organizations are raving about tenfold‘s speed and efficiency.