What Is Segregation of Duties (SoD)?
Segregation of duties (SoD) is an internal control designed to stop conflicts of interest and abuses of power within an organization. SoD ensures that conflicting tasks such as submitting and approving a purchase order must be split between at least two different individuals. This prevents a single employee from being able to circumvent internal controls and commit fraud.
What Is Segregation of Duties?
Segregation of duties (SoD), also known as separation of duties, is an internal control designed to stop conflicts of interest and the misuse of privileges. Segregation of duties prevents too much power from being placed in one person’s hands by requiring businesses to split tasks with the potential for fraud or abuse across two or more individuals. For example, a financial report should not be submitted and reviewed by the same person.
As part of an organization’s internal controls and access control policy, businesses processes and decisions should be reviewed by at least one other person (four eyes principle). Independent controls are essential to prevent theft, fraud and risky behavior such as financial speculation with company assets. Segregation of duties is especially important when it comes to finances, purchase orders and customer data.
Potential problems that can arise without segregation of duties include HR staff that can adjust their own salary or team members in procurement who place and approve fraudulent orders (for example to earn kickbacks). Alongside rules on gifts and gratuity, segregation of duties is an essential part of any business’ compliance strategy.
Examples of conflicts of interests that segregation of duties prevents:
Employees cannot approve their own expense reports.
Business proposals and risk assessments are created by different people.
Financial transactions are independently reviewed.
HR staff cannot adjust their own salary levels.
Download Our Access Control Policy Template
Use our policy template as a starting point to create your own access control policy based on NIST and ISO requirements.
Is Segregation of Duties Mandatory?
Preventing fraud through the use of SoD is not only in the self-interest of businesses, but a legal requirement in many industries. For publicly traded companies, the SOX Act sets out rules ensuring the independent review of financial reports. SoD is also a key requirement in the financial sector, where independent risk assessments are required to comply with GLBA and form an integral part of successful risk management .
Segregation of duties also plays an important role in many IT security standards like ISO 27001, NIST 800-53 or the NIST Cybersecurity Framework. Splitting important tasks across different users and enforcing the principle of least privilege prevents attackers from gaining total control over your network by compromising a single account.
How Does Segregation of Duties Work?
Enforcing SoD requires businesses to ensure that conflicting duties – i.e. a combination of tasks that could enable fraud, abuse or cover-ups – are not assigned to a single person. Some tasks, such as handling large sums of money, are inherently high-risk on their own and must be secured through independent review and approval workflows. In order to enforce these controls, organizations must know
which accounts exist within their IT network
which privileges they hold and
which permissions are incompatible with which other permissions.
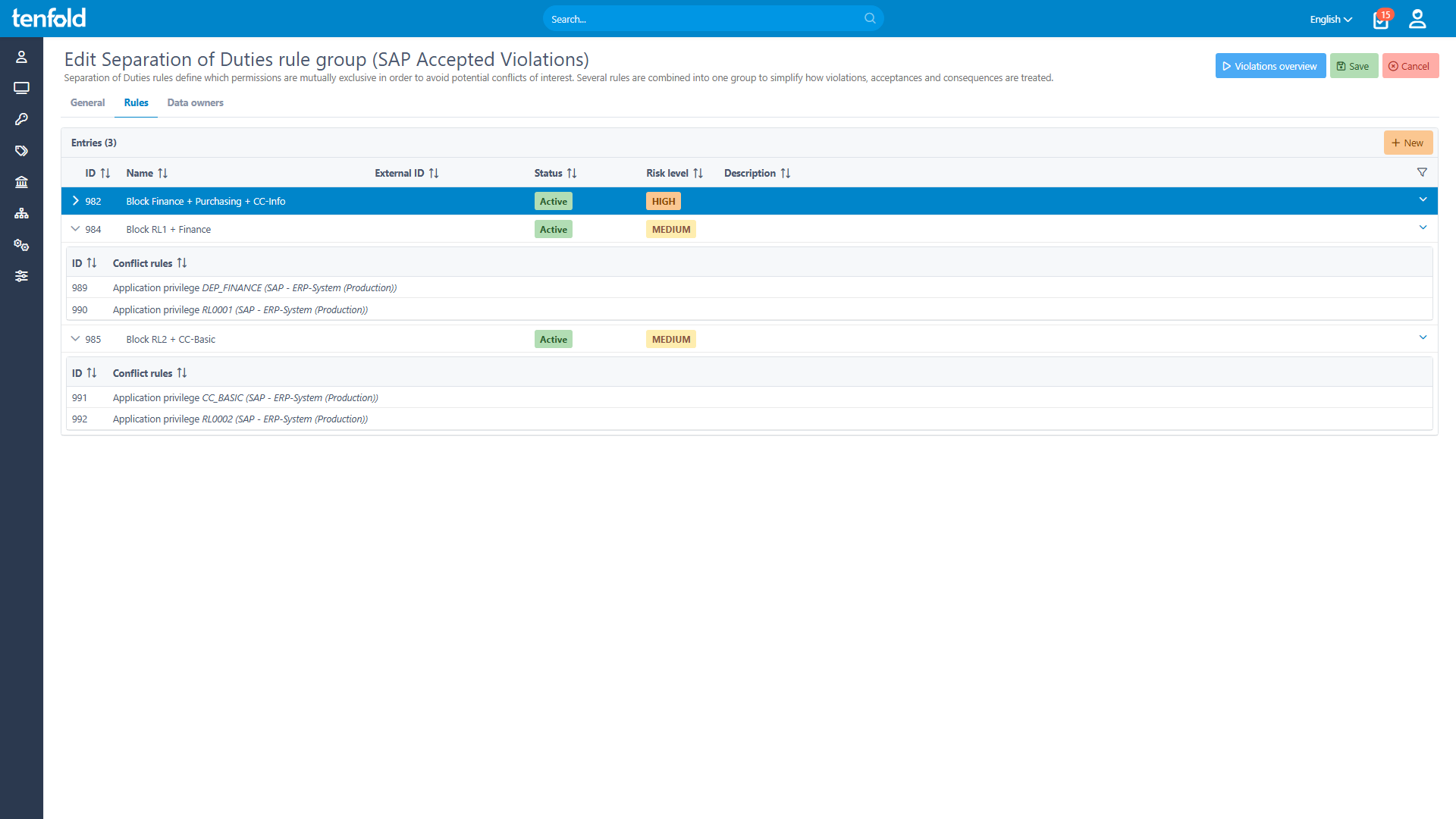
Segregation of Duties: Rules & Consequences
The first step to enforcing segregation of duties is to create SoD rules for your organization. Effectively, an SoD rule lists which access privileges create risk when assigned alongside each other and which actions the organization must take to mitigate that risk.
Typically, the easiest way to resolve SoD rule violations is to simply block conflicting privileges from being assigned. However, sometimes an organization might choose compensating controls instead, such as granting access temporarily or enforcing additional security checks. This can be helpful especially for smaller organizations that face staff limitations in certain roles.
For example: If only two people manage a particular business application and they normally split operational and control functions between them, what do you do if one of them is out office? To address cases like these, organizations need the ability to set alternative controls or short-term exceptions.
Segregation of Duties Matrix
An SoD matrix allows organizations to visualize which business processes conflict with each other by laying them out across the X and Y axis of a table or spreadsheet. For example, let’s look at a simple SoD matrix for the process of submitting and approving equipment orders.
| Job Function | Create Requisition | Approve Requisition | Create Purchase Order | Approve Purchase Order |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Create Requisition | ##### | High Risk | Low Risk | Low Risk |
| Approve Requisition | High Risk | ##### | Low Risk | Low Risk |
| Create Purchase Order | Low Risk | Low Risk | ##### | High Risk |
| Approve Purchase Order | Low Risk | Low Risk | High Risk | ##### |
As you can see, this SoD matrix identifies two scenarios as high-risk: For the same person to both create and approve a requisition, or for the same person to create and approve a purchase order. However, if another person is in the loop during these steps, there is a much lower risk to other overlaps such as an employee submitting a requisition and later approving the final purchase order created by another team member.
Create & Enforce SoD Rules with tenfold!
tenfold makes it easy to implement segregation of duties, detect rule breaks, determine consequences and manage workflows for approving temporary exceptions. Create and manage SoD rules through the same convenient IGA platform that allows you to automate user lifecycles, offer self-service requests and conduct periodic access reviews!
Set individual, multiple or specific combinations of privileges into conflict with each other using our flexible rule editor. Apply tags to privileges to more easily target them with SoD rules or other governance features. Detect and remediate existing rule breaks when you create a new SoD rule. Our no-code governance suite makes stopping conflicts of interest easier than ever before.